Blog Post
Data Protection Day 2024: Five steps to taking control of your data
January 28, 2024, is Data Protection Day, an event recognized by several nations worldwide focused on raising awareness of data protection and promoting best practice for safeguarding privacy and data security for individuals and organizations alike.
In this article, we will explore the history of Data Protection Day and explain why data protection matters for organizations. We will also share five key steps to taking control of your data, doing what you can to protect the personal information of your customers, clients and colleagues.
What is Data Protection?
Data protection is the process of safeguarding the rights and freedoms of individuals in the digital age, especially regarding their personal data. Personal data is any information that relates to an identified or identifiable person, such as name, email, phone number, location, health records or online activity. Data protection laws aim to ensure that personal data is used fairly, lawfully and transparently, and that individuals have control over their own data.
Data protection is not only important for individuals, but also for organizations that collect, store, process or share personal data. Data protection can help organizations enhance their cybersecurity and reduce data risk, preserve their reputation, save time and money, and enhance customer trust. As such, it's essential that they comply with their legal and ethical obligations. Data protection can also foster innovation, efficiency and security across all industry sectors and domains that rely on personal information for their operations and services.
However, data protection also faces many risks and challenges in the modern world, from data breaches and cyber-attacks to manipulation and fraud. These threats can harm the privacy, dignity and well-being of individuals, as well as the security, stability and competitiveness of organizations. Data protection requires constant vigilance, awareness and action from all stakeholders, including individuals, organizations, data protection authorities, policymakers and society as a whole.
The history of Data Protection Day
Data Protection Day has its roots in the Council of Europe’s Convention 108, the first legally binding international treaty on data protection, which was opened for signature on January 28, 1981. Convention 108 established the basic rules for the protection of personal data, such as the right to access, rectify and erase one’s own data, the obligation for organizations to obtain consent for data processing, and the requirement to ensure data security and confidentiality.
In 2006, the Council of Europe decided to launch Data Protection Day, an annual event to celebrate and promote data protection awareness and best practices among the public, the media and the authorities. The date of January 28 was chosen to commemorate the signing of Convention 108. The first Data Protection Day was held on January 28, 2007, with the participation of 47 countries, including all the member states of the Council of Europe and the European Union.
Since then, Data Protection Day has grown into a global phenomenon, with more than 100 countries joining the celebration, including Canada, the United States, India, Japan and Australia. Data Protection Day has also become an occasion to highlight the achievements and challenges of data protection in the digital era, and to foster dialogue and cooperation among various stakeholders, such as data protection authorities, policymakers, civil society, academia and the private sector.
Data Protection Day continues to evolve and adapt to the changing needs and expectations of the data protection community and the society at large. Data Protection Day 2024 will mark the 43rd anniversary of Convention 108, and the 18th edition of the event. It will also coincide with the 75th anniversary of the Council of Europe, the leading human rights organization in Europe.
Why Data Protection matters
Data protection is not only a legal necessity, but also a crucial factor for the success and sustainability of any organization that deals with personal data. Organizations that collect and process personal data have to comply with data protection laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the Data Protection Act 2018 in the UK. More than 137 countries have enacted data protection and privacy laws, while several more are developing legislation. According to Gartner, 75% of the global population will have their data protected under privacy and data protection laws by the end of 2024.
Data protection laws aim to safeguard the rights and freedoms of individuals by ensuring that their personal information is used fairly, lawfully and transparently.
Organizations that respect data protection principles and practices can benefit from:
- Enhanced cybersecurity and reduced data risk: Data protection can help organizations improve their overall cybersecurity posture and reduce data risk through the application of technical controls that help secure and protect sensitive data and business systems from insider threats and external cyber-attack.
- Saving time and money: Data protection can help organizations avoid costly fines, lawsuits, and reputational damage that can result from data breaches, cyber-attacks, or noncompliance. Data protection can also help organizations optimize their data management and storage and reduce unnecessary or redundant data processing.
- Enhancing trust and reputation: Data protection can help organizations build and maintain trust and loyalty with their customers, clients, partners, and employees. Data protection can also help organizations differentiate themselves from their competitors and demonstrate their social responsibility and ethical values.
- Complying with the law: Data protection can help organizations meet their legal and ethical obligations, avoiding sanctions or penalties from data protection authorities. Data protection can also help organizations align with the international standards and best practices on data protection and facilitate cross-border data transfers and cooperation.
Five steps to taking control of your data
To help organizations take control of their data and achieve data protection excellence, we have identified the five key steps that can help you take control of your data:
Step 1: Identification
First, identify where personal data is located across the organization, whether it is stored on-premises or in the cloud, on servers, desktops, databases, email platforms or other data sources. To do this, organizations need a reliable and comprehensive data discovery tool that can scan and find personal data across the broadest range of structured and unstructured data types.
Step 2: Verification
Second, verify data discovery findings with the key stakeholders, such as data owners, data custodians or data protection officers. This step also involves risk assessing and scoring data assets and classifying them based on their sensitivity. This verification process informs how data will be treated in the next step, particularly data that has been found in exposed locations.
Step 3: Remediation
Third, remediate any data issues that are identified in the previous steps, such as unexpected stores of sensitive and personal information, unauthorized data stores or data that is redundant, trivial and/or obsolete (ROT). Remediation can involve various actions, such as masking, encrypting, deleting or quarantining data, depending on the data type, and its location and purpose. Often remediation tasks will need to be delegated to data owners to authorize, which can be facilitated through tools like Enterprise Recon.
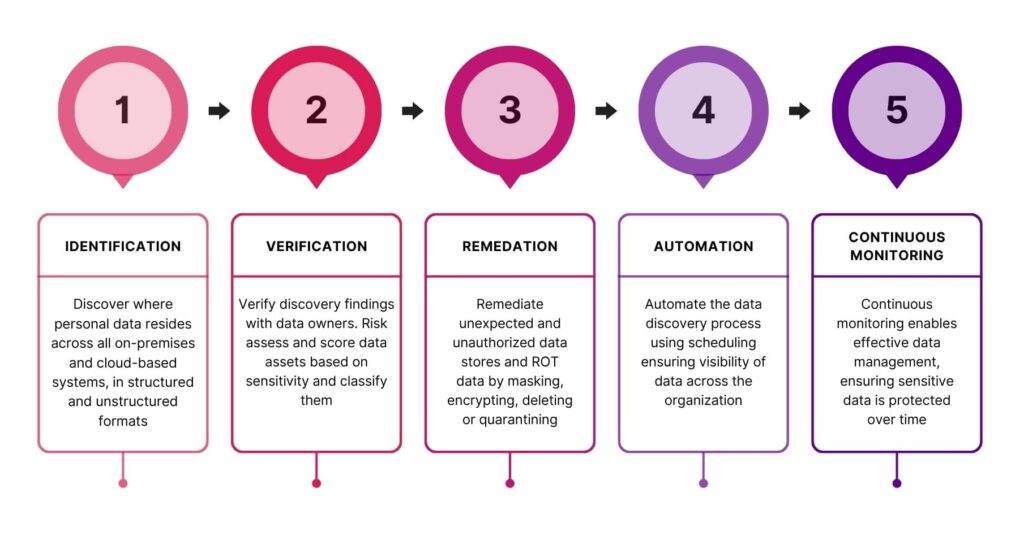
Step 4: Automation
Fourth, automate the data discovery process. This sets the foundations for an effective data management program. Automating the discovery process helps to reduce the resource overhead of configuring and delivering discovery scanning while ensuring visibility of data across the organization. Automation can be achieved by using scheduling features based on a pre-configured scope, allowing recurring scans across the environment continuously or at regular intervals.
Step 5: Continuous monitoring
The fifth and final step is to monitor the data stores and data flows continuously, to ensure that data protection is maintained and improved over time, and to respond to any changes or challenges that may arise.
Continuous monitoring can be achieved with frequent, automated discovery scans, which can identify and report any new or rogue data that may appear in the organization. Further, reporting from frequent discovery scanning can be used as part of assurance and compliance programs, demonstrating robust data management procedures across the business.
Data protection is not a one-time event, but a continuous process that requires constant monitoring and rapid action to ensure that individuals’ data rights are upheld and their privacy is protected through appropriate data security controls and data management practices.
Commit to Data Protection on January 28, 2024
Data Protection Day 2024 is an opportunity to celebrate the achievements and progress of data protection, and to reaffirm the commitment and responsibility of organizations and all with data protection responsibilities to protect the rights and freedoms of individuals in the digital age.
This Data Protection Day, take control of your data with Ground Labs. Book a call with one of our experts and find out how.
