Enterprise Recon 2.1
Exchange Domain
This section covers the following topics:
- Overview
- Licensing
- Requirements
- Add an Exchange Domain Target
- Scan Additional Mailbox Types
- Archive Mailbox and Recoverable Items
- Unsupported Mailbox Types
- Configure Impersonation
- Mailbox in Multiple Groups
Overview
The Exchange Domain Target allows you to scan mailboxes and mailbox Groups by specifying the domain on which the mailboxes reside on.
To scan a Microsoft Exchange server directly, see Microsoft Exchange (EWS) for more information.
Licensing
For Sitewide Licenses, all scanned Exchange Domain Targets consume data from the Sitewide License data allowance limit.
See Target Licenses for more information.
Requirements
| Requirements | Description |
|---|---|
| Version Support | Exchange Server 2007 and above. |
| Proxy Agent |
Required Proxy Agents:
|
| TCP Allowed Connections |
|
| Service Account | The account used to scan Microsoft Exchange mailboxes must:
|
Add an Exchange Domain Target
- From the New Scan page, Add Targets.
- In the Select Target Type dialog box, select Exchange Domain.
- Fill in the following fields:
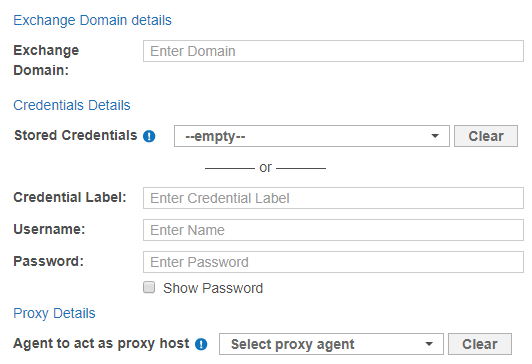
Field Description Domain Enter a domain to scan mailboxes that reside on that domain. This is usually the domain component of the email address, or the Windows Domain. Credential Label Enter a descriptive label for the credential set. Username Enter your service account user name. Password Enter your service account password. Agent to act as proxy host Select a Windows Proxy Agent. - Click Test. If ER2 can connect to the Target, the button changes to a Commit button.
- Click Commit to add the Target.
- Back in the New Search page, locate the newly added Exchange Domain Target and click on the arrow next to it to display a list of available mailbox Groups. Expand a Group to see a list of mailboxes that belong to that Group.
- Select Groups or mailboxes to add them to the "Selected Locations" list.
- (Optional) You can add a location manually by selecting + Add New Location at the bottom of the list, clicking Customise and entering <Group/User Display Name> in the Exchange Domain field.
- Click Next to continue setting up your scan.
Scan Additional Mailbox Types
The following additional mailbox types are supported:
- Shared mailboxes. Shared mailboxes do not have a specific owner. Instead, user accounts that need to access the shared mailbox are assigned "SendAs" or "FullAccess" permissions.
- Linked mailboxes. A linked mailbox is a mailbox that resides on one Active Directory (AD) forest, while its associated AD user account (the linked master account) resides on another AD forest.
- Mailboxes associated with disabled AD user accounts. Disabled AD user accounts may still be associated with active mailboxes that can still receive and send email. Mailboxes associated with disabled AD user accounts are not the same as disconnected mailboxes.
- Archive Mailbox and Recoverable Items
To scan the above supported mailbox types, use a service account with “FullAccess” rights to the target mailbox.
The following sections contain instructions on how to grant "FullAccess" permissions for each mailbox type:
Changes may not be immediate. Wait 15 minutes before starting a scan on the exchange server.
Once the service account is granted access to the target mailboxes, follow the instructions above to add the shared mailbox as a Target.
You cannot use a linked master account (the owner of a linked mailbox) to scan Exchange Targets in ER2. To successfully scan an Exchange Target, use a service account that resides on the same AD forest as the Exchange Target.
Shared Mailboxes
To grant a service account "FullAccess" rights to shared mailboxes, run the following commands in the Exchange Management Shell:
-
To grant a user full access to a specific shared mailbox:
Add-MailboxPermission -Identity <SHARED_MAILBOX> -User <SERVICE_ACCOUNT> -AccessRights FullAccess -Automapping $falsewhere <SHARED_MAILBOX> is the name of the shared mailbox, and <SERVICE_ACCOUNT> is the name of the account used to scan the mailbox. -
To grant a user full access to all existing shared mailboxes on the Exchange server:
Get-Recipient -Resultsize unlimited | where {$_.RecipientTypeDetails -eq "SharedMailbox"} | Add-MailboxPermission -User <SERVICE_ACCOUNT> -AccessRights FullAccess -Automapping $falsewhere <SERVICE_ACCOUNT> is the name of the account used to scan the mailboxes.
Linked Mailboxes
To grant a service account "FullAccess" rights to linked mailboxes, run the following commands in the Exchange Management Shell:
-
To grant a user full access to a specific shared mailbox:
Add-MailboxPermission -Identity <LINKED_MAILBOX> -User <SERVICE_ACCOUNT> -AccessRights FullAccess -Automapping $falsewhere <LINKED_MAILBOX> is the name of the shared mailbox, and <SERVICE_ACCOUNT> is the name of the account used to scan the mailbox. -
To grant a user full access to all existing shared mailboxes on the Exchange server:
Get-Recipient -Resultsize unlimited | where {$_.RecipientTypeDetails -eq "LinkedMailbox"} | Add-MailboxPermission -User <SERVICE_ACCOUNT> -AccessRights FullAccess -Automapping $falsewhere <SERVICE_ACCOUNT> is the name of the account used to scan the mailboxes.
Mailboxes associated with disabled AD user accounts
To grant a service account "FullAccess" rights to mailboxes associated with disabled AD user accounts, run the following commands in the Exchange Management Shell:
-
To grant a user full access to a specific mailbox:
Add-MailboxPermission -Identity <USER_DISABLED_MAILBOX> -User <SERVICE_ACCOUNT> -AccessRights FullAccess -Automapping $falsewhere <USER_DISABLED_MAILBOX> is the name of the mailbox associated with a disabled AD user account, and <SERVICE_ACCOUNT> is the name of the account used to scan the mailbox.
Archive Mailbox and Recoverable Items
Requirements: Exchange Server 2010 SP1 and newer.
When enabled for a user mailbox, the Archive mailbox and the Recoverable Items folder can be added to a scan:
- Archive or In-Place Archive mailboxes.
An archive mailbox is an additional mailbox that is enabled for a user's primary mailbox, and acts as long-term storage for each user account.
Archive mailboxes are listed as (ARCHIVE) on the Select Locations page when browsing an Exchange mailbox. - Recoverable Items folder or dumpster.
When enabled, the Recoverable Items folder or the dumpster in Exchange retains deleted user data according to retention policies.
Recoverable Items folders are listed as (RECOVERABLE) on the Select Locations page when browsing an Exchange mailbox.
By default, adding a user mailbox to a scan also adds the user's Archive mailbox and Recoverable Items folder to the scan.
To add only the Archive mailbox or Recoverable Items folder to the scan:
- Configure impersonation for the associated user mailbox. See Configure Impersonation for more information.
- Add the Exchange Target to the scan.
- In the Select Locations page, expand the added Exchange Target and browse to the Target mailbox.
- Expand the target mailbox, and select (ARCHIVE) or (RECOVERABLE).
Unsupported Mailbox Types
ER2 currently does not support the following mailbox types:
- Disconnected mailboxes. Disconnected mailboxes are mailboxes that have been:
- Disabled. Disabled mailboxes are rendered inactive and retained until the retention period expires, while leaving associated user accounts untouched. Disabled mailboxes can only be accessed by reconnecting the owner user account to the mailbox.
- Removed. Removing a mailbox deletes the associated AD user account, renders the mailbox inactive and retains it until its retention period expires. Removed mailboxes can only be accessed by connecting it to another user account.
- Moved to a different mailbox database. Moving a mailbox from one mailbox database to another leaves the associated user account untouched, but sets the state of the mailbox to "SoftDeleted". "SoftDeleted" mailboxes are left in place in its original mailbox database as a backup, in case the destination mailbox is corrupted during the move. To access a "SoftDeleted" mailbox, connect it to a different user account or restore its contents to a different mailbox.
- Resource mailboxes. Resource mailboxes are mailboxes that have been assigned to meeting locations (room mailboxes) and other shared physical resources in the company (equipment mailboxes). These mailboxes are used for scheduling purposes.
- Remote mailboxes. Mailboxes that are set up on a hosted Exchange instance, or on Microsoft 365, and connected to a mail user on an on-premises Exchange instance.
- System mailboxes.
- Legacy mailboxes.
The following are not mailboxes, and are not supported as scan locations:
- All distribution groups.
- Mail users or mail contacts.
- Public folders.
Configure Impersonation
To scan a Microsoft Exchange mailbox, you can:
- Use an existing service account, and assign it the ApplicationImpersonation management role, or
- (Recommended) Create a new service account for use with ER2 and assign it the ApplicationImpersonation management role.
Service accounts are user accounts set up to perform administrative tasks only. Because of the broad permissions granted to service accounts, we recommend that you closely monitor and limit access to these accounts.
Assigning a service account the ApplicationImpersonation role allows the account to behave as if it were the owner of any account that it is allowed to impersonate. ER2 scans those mailboxes using permissions assigned to that service account.
To assign a service account the ApplicationImpersonation role for all mailboxes:
-
On the Exchange Server, open the Exchange Management Shell and run as administrator:
# <impersonationAssignmentName>: Name of your choice to describe the role assigned to the service account. # <serviceAccount>: Name of the Exchange administrator account used to scan EWS. New-ManagementRoleAssignment –Name:<impersonationAssignmentName> –Role:ApplicationImpersonation –User:<serviceAccount>
(Advanced) To assign the service account the ApplicationImpersonation role for a limited number of mailboxes, apply a management scope when making the assignment.
To assign a service account the ApplicationImpersonation role with an applied management scope:
- On the Exchange Server, open the Exchange Management Shell as administrator.
-
Create a management scope to define the group of mailboxes the service account can impersonate:
New-ManagementScope -Name <scopeName> -RecipientRestrictionFilter <filter>For more information on how to define management scopes, see Microsoft: New-ManagementScope. -
Apply the ApplicationImpersonation role with the defined management scope:
New-ManagementRoleAssignment –Name:<impersonationAssignmentName> –Role:ApplicationImpersonation –User:<serviceAccount> -CustomRecipientWriteScope:<scopeName>
Mailbox in Multiple Groups
If a mailbox is a member of multiple Groups, it is scanned each time a Group it belongs to is scanned. Mailboxes that are members of multiple Groups still consume only one mailbox license, no matter how many times it is scanned as part of a separate Group.